Blocked fallopian tubes can be seen in 15% in infertile ladies. Fallopian tubes are important part of female reproductive system, that helps in transportation of gametes, fertilisation of egg and sperm, and provide nutrition to the developing embryo. In this blog, we shall discuss on following matters:
- Role of Fallopian tube in human reproduction
- Various Tubal patency tests
- Advantages and disadvantages of each tubal patency test
- Various Treatment options for blocked tubes
Fallopian tubes are two in number, i.e. one on each side, connecting the uterus at cornual region. During coitus, the sperms are released in the posterior fornix of the vagina. Around lakhs of sperms can pass through cervix and reach the uterus. From there, only around 100-1000 sperms can survive and travel through the fallopian tubes to reach the ampullary region of the tube, where the egg is waiting. The egg also known as ovum is released every month from the ovary, which is then captured by the fallopian tube.
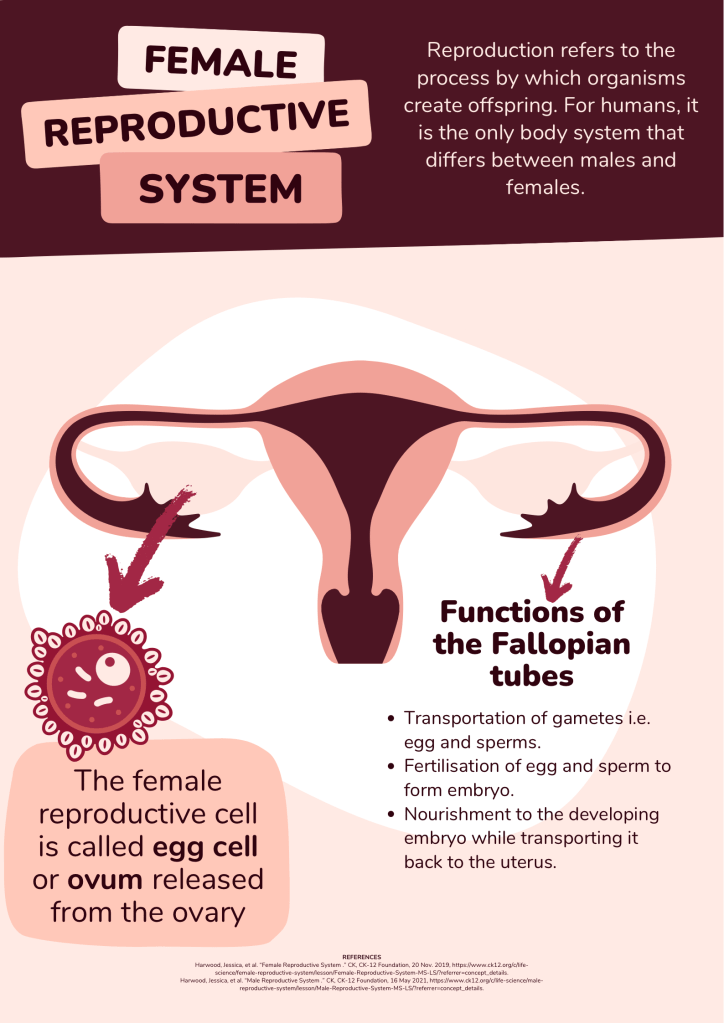
How to check if fallopian tubes are working well?
The function of ovaries and uterus can be checked to some extend with the help of transvaginal ultrasound (TVS). However, TVS can not detect the pathology of fallopian tubes, unless they are swollen enough to be seen on ultrasound as hypo-echoic collection adjacent to the uterus, condition known as hydrosalpinx. Tubal patency tests is done to check the patency of fallopian tubes.
What are tubal patency tests?
Tubal patency tests work on the principle of injecting fluid through the uterus into the tubes, and later to see if this fluid can be passed through these tubes. They are of three types:
- Hysterosalpingeography (HSG)
- Saline sonosalpingeography (SSG)
- Hysterosalpingocontrast sonography (HyCoSy)
- Laparoscopy
Hysterosalpineography (HSG)
HSG is the most commonly used tubal patency test. It is an X-ray based procedure. An oil soluble contrast medium (OSCM) that is composed of iodinated ethyl esters of fatty acids found in poppy seeds was used since 1925 till 1950s, when water soluble contrast medium (WSCM) also came into the market. OSCM has a disadvantage of venous intravasation of the contrast material and rare risk of embolisation. However, OSCM has proven fertility enhancing effect compared with WSCM.
Procedure:
The contrast dye is injected through the cervix with the help of special metallic instrument, i.e. HSG cannula. Repeated X-ray films are taken, to see if the dye could pass through uterus, tubes and eventually inside the abdominal cavity.
This procedure is quiet painful.
Some ladies may experience fainting attacks too. This can be taken care of by giving Injection atropin, sedation and a painkiller prior to the procedure.
HSG costs around 2.5K to 3.5K INR.
It has 70% accuracy in detecting blocked tubes with high chances of false results due to physiological cornual spasm.
Saline sonosalpingeography (SSG)
It is an ultrasound based technique that uses normal saline instead of contrast dye. Thus, it is less painful. It has an added advantage that, it can also be done under anaesthesia, making it completely painless. On ultrasound, the free fluid seen as black shadow behind the uterus concludes that at least one fallopian tube is patent.
It is also a good measure to detect uterine space occupying lesion like polyp, septum, adhesions, etc.
It costs around 10K to 15K INR.
Hysterosalpingocontrast sonography (HyCoSy)
It is also an ultrasound based technique that uses special contrast dye like echovist, etc. for enhanced resolution. It can also be done under anaesthesia, therefore, can be completely painless.
It can also detect uterine polyps, septum, adhesions with greater sensitivity and specificity.
Transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy (THL)
Laparoscopy and transvaginal tubal flushing with normal saline is a definitive diagnostic procedure with 100% sensitivity.
It is a short day care procedure, done under anaesthesia.
It has an added advantage that addition pelvic and or peritoneal pathology can also be identified and treated in the same sitting.
However, it is an invasive, and comparatively costlier procedure and can cost around 25K to 50K INR.
Side-effects of tubal patency tests:
- Pain
- Infection
- Syncopal attack
Treatment of Blocked tubes
Blocked tubes can be treated with the help of surgery i.e. laparoscopy. However, the success rate of laparoscopic tubal reconstruction surgery is limited and is around 9-25%. Success rate of proximal tubal block surgery i.e. hysteroscopic tubal cannulation is comparative higher than distal tubal surgeries like laparoscopic fimbrioplasty.
Also, long standing tubal disease has poor prognosis in terms of pregnancy rate. The presence of hydrosaplinx is contraindicated for laparoscopic tubal corrective surgeries.
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is another treatment for ladies with blocked tubes who are eager to get pregnant. The success rate of IVF in such patients can be as high as 50-80% depending upon other cause of infertility.
Since, IVF procedure does not involve the direct role of fallopian tubes, and the fertilisation of egg and sperm occurs in vivo inside a special IVF lab, blocked tubes does not hamper its success rate. However, presence of hydrosalpinx have a negative impact on the success rate of embryo transfer, therefore, laparoscopic tubal clipping before embryo transfer may be mandatory in few cases.
Conclusion
Since fallopian tubes play an important role in human reproduction, tubal patency test becomes a necessary test in the initial work up of an infertile lady. It can be done with the help of X-ray, ultrasound, or laparoscopy.
HSG, most commonly used tubal patency test, is X-ray based, cheaper, and painful test. SSG is ultrasound based test, costlier and can be painless. HyCoSy is a newer tubal patency test, that is done with a costly dye, and is not available in many centres. Laparoscopy is 100% diagnostic test and is invasive and costly.
IVF remains the main treatment option for blocked tubes. In certain cases, tubal corrective surgery can also be done.
Read more: Blocked tubes! What next??https://wordpress.com/post/dranadeepchandiivfspecialist.wordpress.com/58

Leave a comment